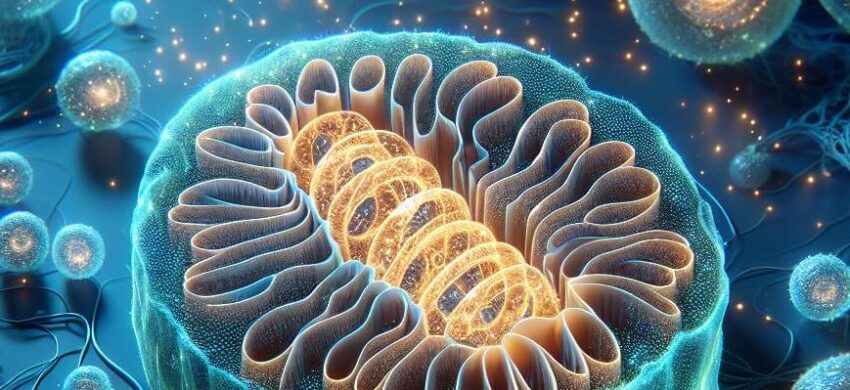
This cellular component, often referred to as the “powerhouse,” orchestrates energy production, critical for maintaining cellular health and function. Their unique structure allows these operations, wherein a double-membrane construction is noted. The outer layer serves as a protective barrier, while the inner membrane contains numerous folds, called cristae, dramatically increasing surface area for energy production.
Within the membrane, a matrix comprising enzymes, ribosomes, and mitochondrial DNA exists, indulging in diverse biochemical reactions. The primary derivative is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), serving as the cell’s primary energy currency. The electron transport chain facilitates ATP generation, effectively carrying electrons down a series of reactions.
Additionally, these structures play a pivotal role in other cellular processes, including cell signalling, cell growth, and even programmed cell death (apoptosis). Furthermore, owing to their own DNA, they replicate independently of the cell, contributing to genetic variation and inheritance patterns. Hence, their structure ideally positions them as central role players in cellular energetics and biological function.
 |
 |
 |